a circular economy with no waste
The concepts of zero waste and circular economy
What is zero waste ?
“Zero Waste is a goal that is both pragmatic and visionary, to guide people to emulate sustainable natural cycles, where all discarded materials are resources for others to use. Zero Waste means designing and managing products and processes to reduce the volume and toxicity of waste and materials, conserve and recover all resources, and not burn or bury them. Implementing Zero Waste will eliminate all discharges to land, water, or air that may be a threat to planetary, human, animal or plant health. ”
– Definition of Zero Waste as adopted by the Zero Waste International Alliance
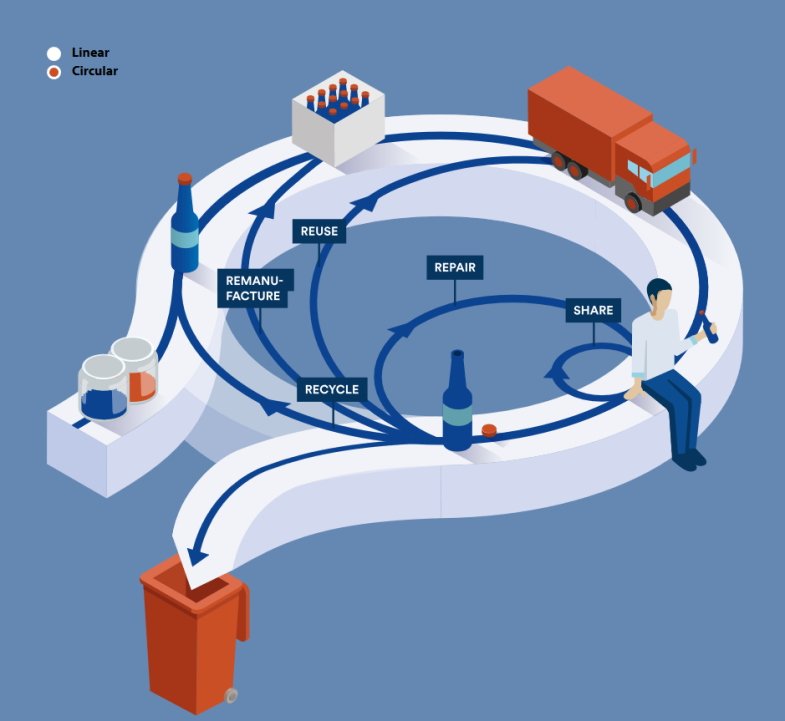
ZERO WASTE GOAL
The zero waste goal is a restorative and regenerative economy that keeps products, materials and components at their highest utility and value at all times—a circular economy with no waste. We should always aim at making the best possible use of materials: in some contexts, it will be possible to reduce the use of materials and reuse secondary raw resources, in some other contexts regulating waste disposal is the best possible achievement (at the current time).
CIRCULAR ECONOMY
A circular economy is a system in which resource input and waste, emission, and energy leakage are minimized by slowing, closing, and narrowing material and energy loops. This can be achieved by redefining products and services to design waste out while minimizing negative impacts – such as long-lasting design, maintenance, repair, reuse, re-manufacturing, refurbishing, and recycling.
Zero Waste Hierarchy
Follow the steps towards more sustainable resource management.
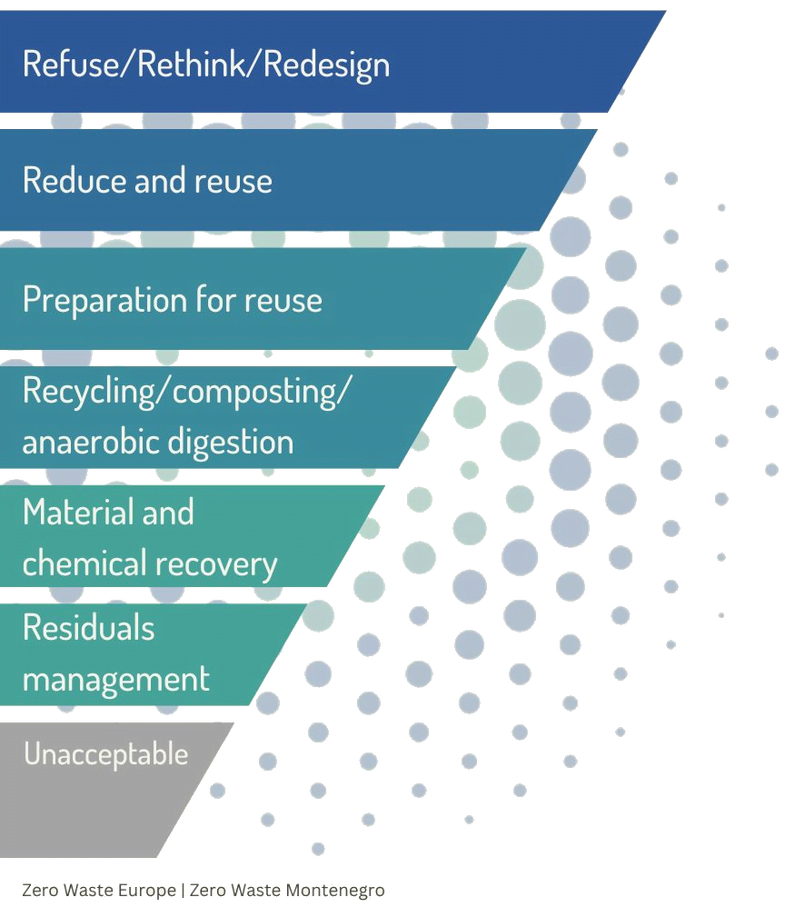
Refuse what we don’t need and change the way we produce and consume by redesigning business models, goods and packaging in order to reduce resource-use and waste.
Minimize the quantity, toxicity and ecological footprint of consumption. Use products or components, that are not waste, for the same purpose for which they were conceived.
Check, clean or repair products or components of products that have become waste so that they can be re-used without any other pre-processing
High quality material recovery from separately collected
waste streams.
Technologies to recover materials from mixed waste and discards from sorting processes into new building blocks for high quality applications.
What cannot be recovered from mixed waste is biologically stabilised prior to landfilling.
Options that don’t allow for material recovery, have high environmental impact and create lock in effects that threaten the transition to Zero Waste: waste to energy incineration, co-incineration, plastic to fuel, landfilling of non-stabilised waste, gasification, pyrolysis, illegal dumping, open burning and littering.
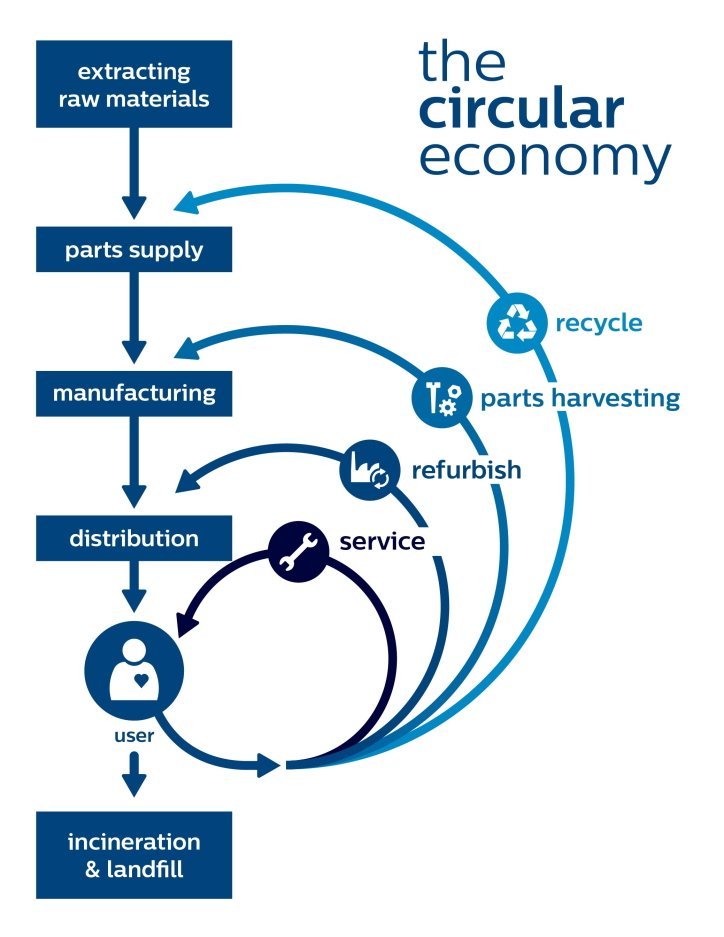
What is circular economy?
“A circular economy is a system in which resource input and waste, emission, and energy leakage are minimized by slowing, closing, and narrowing material and energy loops. This can be achieved by redefining products and services to design waste out while minimizing negative impacts – such as long-lasting design, maintenance, repair, reuse, re-manufacturing, refurbishing, and recycling. Underpinned by a transition to renewable energy sources, the circular model builds economic, natural and social capital. This is in contrast to a linear economy which is a ‘take, make, dispose’ model of production.” …
The Story of Stuff
The 20 minutes video of “The Story of Stuff” (watched more than 8.000.000 times!) explained in a clear and entertaining way the problem with our current linear economy.
Sources:
European Parliamentary Research Service infographics, the circular economy image: Philips USA, The Story of Stuff video, the ZW Hierarchy image: Zero Waste Europe
